
The fallopian tubes are two thin tubes that connect the ovaries to the uterus. They play a crucial role in reproduction.
Fallopian tubes, also called oviducts, are essential for female fertility. These tubes transport the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Fertilization typically occurs within the fallopian tubes, where the sperm meets the egg. Each tube is about 10-12 cm long and is lined with cilia, tiny hair-like structures that help move the egg.
Healthy fallopian tubes are vital for natural conception. Blockages or damage can lead to infertility or ectopic pregnancies. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help maintain fallopian tube health. Understanding their function is key to reproductive health.
Introduction To Fallopian Tubes
The Fallopian tubes are key organs in the female reproductive system. They connect the ovaries to the uterus. These tubes play a crucial role in fertility and conception.
Anatomical Overview
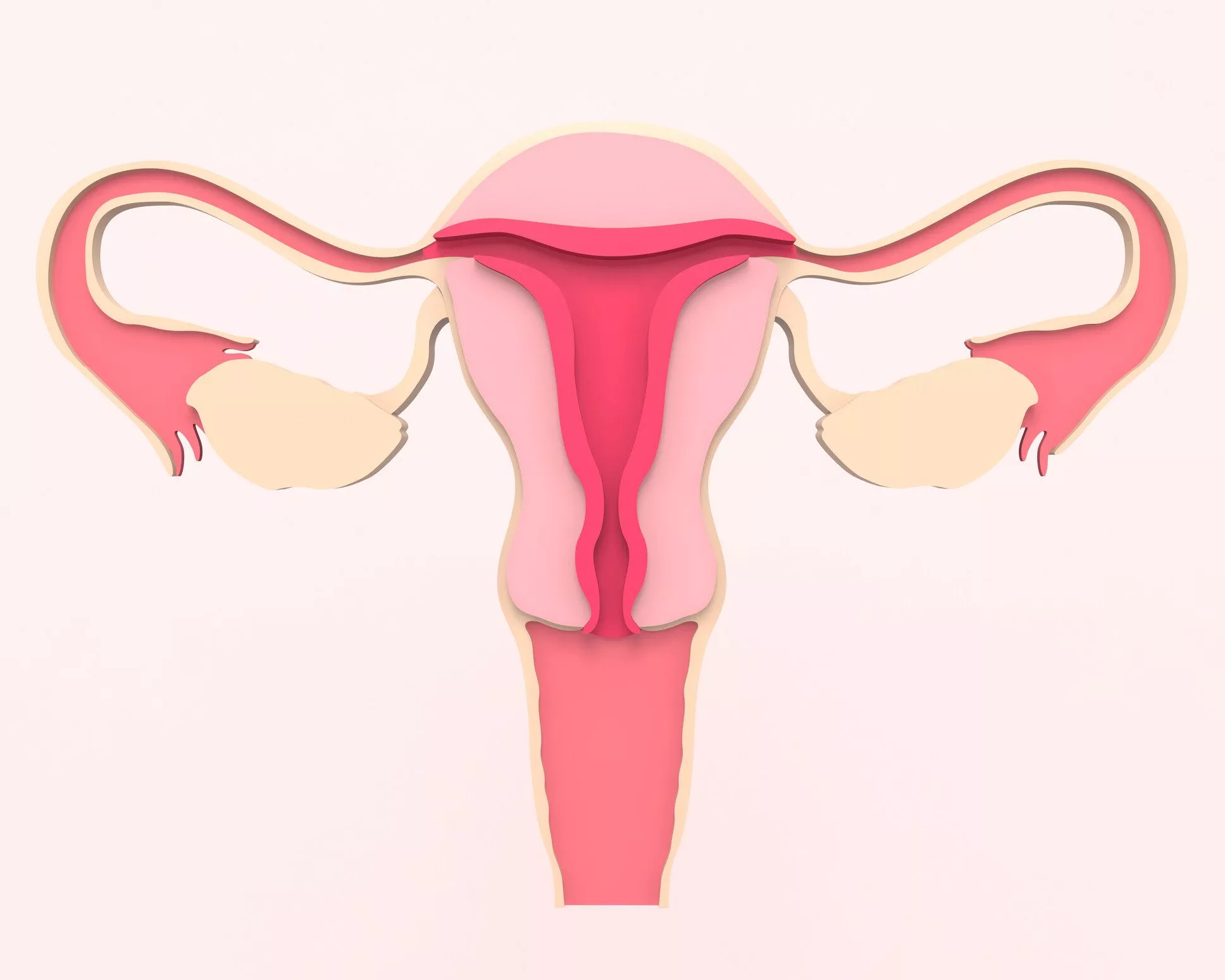
The Fallopian tubes are two thin tubes located on either side of the uterus. Each tube is about 10-12 cm long. They have four main parts: the infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus, and interstitial part.
| Part | Description |
|---|---|
| Infundibulum | Funnel-shaped end near the ovary |
| Ampulla | Widest part, where fertilization usually occurs |
| Isthmus | Narrow part connecting to the uterus |
| Interstitial Part | Section that passes through the uterine wall |
Significance In Reproductive Health
The Fallopian tubes are essential for egg transportation. They also provide the site for sperm to meet the egg. This process is vital for natural conception.
- Transporting the egg from the ovary
- Providing the site for fertilization
- Helping the fertilized egg reach the uterus
If the Fallopian tubes are blocked, it can lead to infertility. Conditions like ectopic pregnancy can also occur, where the fertilized egg implants in the tube.
Maintaining healthy Fallopian tubes is crucial for overall reproductive health. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are recommended.
Credit: www.newhopefertility.com
Structure And Location
The fallopian tubes are essential parts of the female reproductive system. They play a crucial role in transporting eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Located on each side of the uterus, these tubes are about 10-12 cm in length. They are vital for natural conception.
Tube Segments
Each fallopian tube is divided into four segments:
- Infundibulum: This is the funnel-shaped opening near the ovary.
- Ampulla: The widest section where fertilization often occurs.
- Isthmus: A narrow part near the uterus.
- Interstitial (or Intramural): The part that passes through the uterine wall.
Relationship With Ovaries And Uterus
The fallopian tubes are positioned between the ovaries and the uterus. Each tube opens near an ovary and extends toward the uterus. This allows the tube to catch the egg during ovulation.
A table outlining their relationships:
| Part | Location |
|---|---|
| Infundibulum | Near the ovary |
| Ampulla | Middle, widest part |
| Isthmus | Closer to the uterus |
| Interstitial | Within the uterine wall |
The position and structure of the tubes ensure that the egg can travel smoothly. This journey ends at the uterus, where it can implant if fertilized.
Role In Fertilization
The Fallopian tubes play a crucial role in fertilization. They are essential for the journey of both the egg and sperm. Each part of the tube has a specific function to aid fertilization.
Egg Transport
The Fallopian tube is responsible for transporting the egg. After ovulation, the egg is released from the ovary. Tiny hair-like structures called cilia help move the egg along the tube.
The egg travels from the ovary to the uterus. This journey is crucial for fertilization to occur. The egg needs to meet the sperm in the Fallopian tube.
Sperm Passage
The Fallopian tube also facilitates sperm passage. Sperm must travel from the vagina to the Fallopian tube. This journey involves swimming through the cervix and uterus.
Once in the Fallopian tube, sperm meet the egg. Fertilization usually happens in the ampulla, the widest part of the tube. The environment inside the tube supports sperm survival and function.
| Function | Details |
|---|---|
| Egg Transport | Moves the egg from ovary to uterus using cilia. |
| Sperm Passage | Allows sperm to reach the egg for fertilization. |
Early Embryo Development
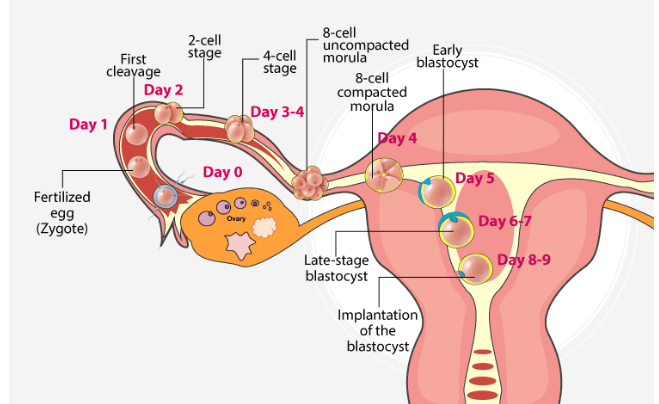
The journey of the embryo begins in the fallopian tubes. This early stage is crucial for the future baby. Let’s dive into the initial steps of this amazing process.
Initial Cell Divisions
Once fertilization happens, the single cell starts to divide. This is known as cleavage. The zygote splits into two cells, then four, and continues. These early divisions are rapid and essential.
During this stage, the cells do not grow in size. Instead, they become smaller with each division. These cells are called blastomeres. The embryo is still in the fallopian tube at this point.
Movement To Uterus
The embryo needs to reach the uterus for further development. The fallopian tube helps in this movement. Tiny hair-like structures called cilia line the tube. They push the embryo towards the uterus.
Meanwhile, the embryo continues to divide and grow. By the time it reaches the uterus, it becomes a blastocyst. The blastocyst has about 100 cells. It is ready for the next stage, implantation.
| Stage | Cells | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Zygote | 1 | Fallopian Tube |
| Blastomere | 2-16 | Fallopian Tube |
| Blastocyst | 100+ | Uterus |
Understanding these stages helps us appreciate the complexity of life. Each step in the fallopian tubes is vital for a successful pregnancy.
Common Infections
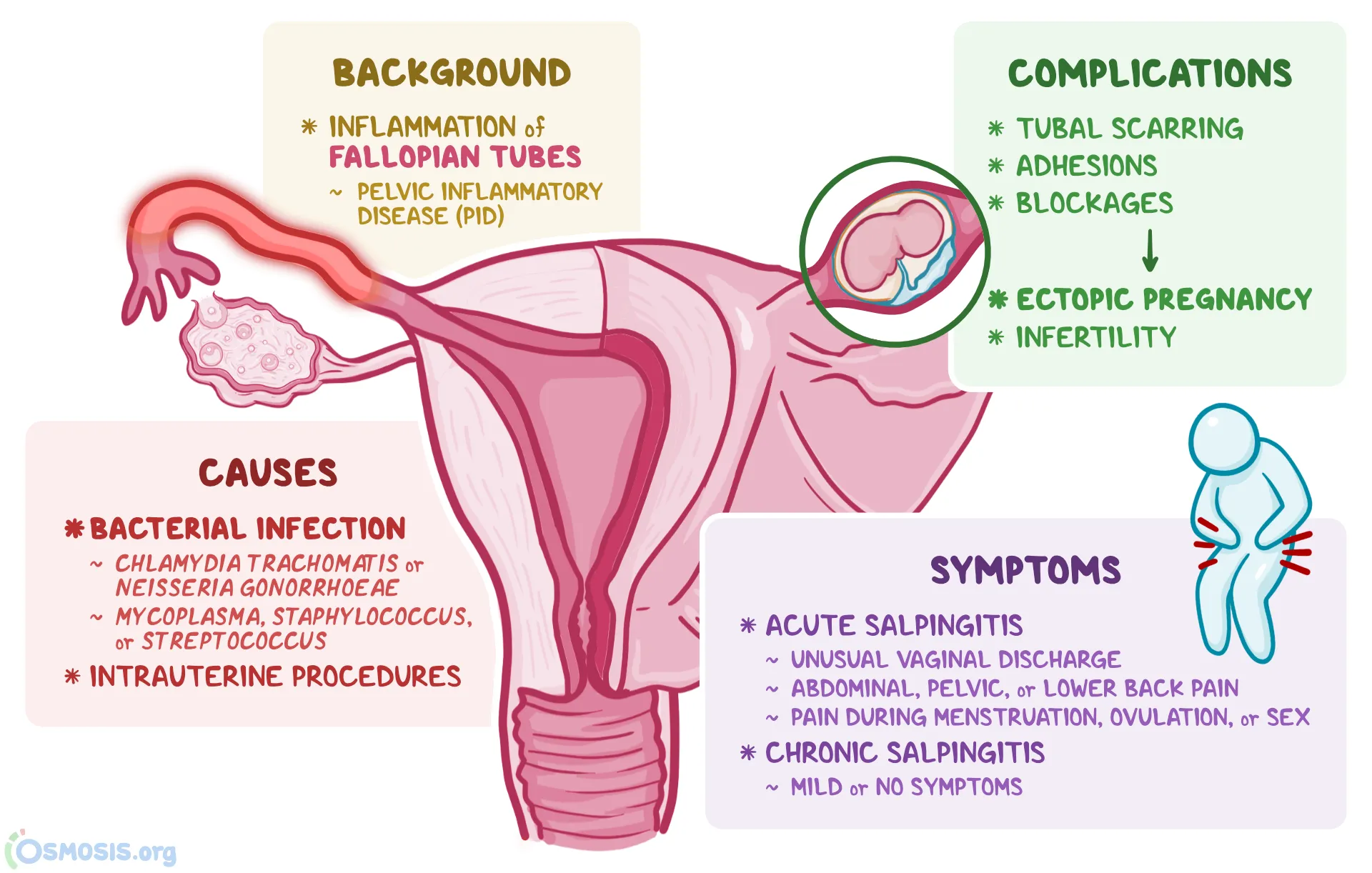
The fallopian tubes are vital reproductive organs. They can be affected by various infections. These infections can lead to serious health issues. This section explores two common infections: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) and Salpingitis.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is a widespread infection. It affects the female reproductive organs. PID can cause severe pain and discomfort.
The main symptoms of PID are:
- Lower abdominal pain
- Fever
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Painful urination
- Pain during intercourse
PID often results from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Gonorrhea and chlamydia are common culprits. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial. Untreated PID can lead to infertility.
Salpingitis
Salpingitis is an infection of the fallopian tubes. It is a type of PID. Salpingitis can cause the tubes to become swollen and blocked.
Common symptoms of Salpingitis include:
- Severe lower abdominal pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Pain during ovulation
Salpingitis is often caused by bacterial infections. STIs are a primary source. Early treatment is vital to prevent complications. Untreated Salpingitis can lead to chronic pain and infertility.
| Infection | Symptoms | Causes | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PID | Abdominal pain, fever, discharge | STIs (Gonorrhea, Chlamydia) | Infertility, Chronic pain |
| Salpingitis | Abdominal pain, fever, nausea | Bacterial infections, STIs | Infertility, Chronic pain |
Understanding these infections is important. Awareness helps in seeking timely medical help. Prevention and early treatment can protect reproductive health.
Blockages And Obstructions
Blockages in the fallopian tubes can prevent pregnancy. The tubes carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Obstructions can block this path, making it hard to conceive.
Causes Of Blockages
Blockages in the fallopian tubes can occur for several reasons. These are the most common causes:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infection can lead to scarring.
- Endometriosis: Tissue growth outside the uterus can block tubes.
- Previous Surgeries: Scars from past operations can cause blockages.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Infections like chlamydia can scar the tubes.
Impact On Fertility
Blockages in the fallopian tubes can severely impact fertility. Here’s how:
| Type of Blockage | Impact on Fertility |
|---|---|
| Partial Blockage | May reduce the chance of pregnancy. |
| Complete Blockage | Makes natural conception impossible. |
Fertility treatments can help. Options include IVF or surgery to remove blockages.
Ectopic Pregnancies
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. This usually happens in the fallopian tubes. This condition is serious and needs immediate medical attention.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Here are some common risk factors:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy: Having had one before raises the risk.
- Inflammation or infection: Infections like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can damage the tubes.
- Fertility treatments: Treatments such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) may increase risk.
- Structural issues: Abnormalities in the fallopian tubes or uterus.
- Smoking: Women who smoke have a higher chance of ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms And Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can be life-saving. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Sharp pain on one side of the abdomen.
- Vaginal bleeding: Light to heavy bleeding is a warning sign.
- Shoulder pain: Pain from a ruptured tube may be felt in the shoulder.
- Weakness or dizziness: These can signal internal bleeding.
Doctors use various methods to diagnose ectopic pregnancies:
- Ultrasound: Detects the location of the pregnancy.
- Blood tests: Measure hCG levels to confirm pregnancy.
- Pelvic exam: Checks for pain, tenderness, and abnormal masses.
If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy, seek medical help immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to avoid complications.
Endometriosis
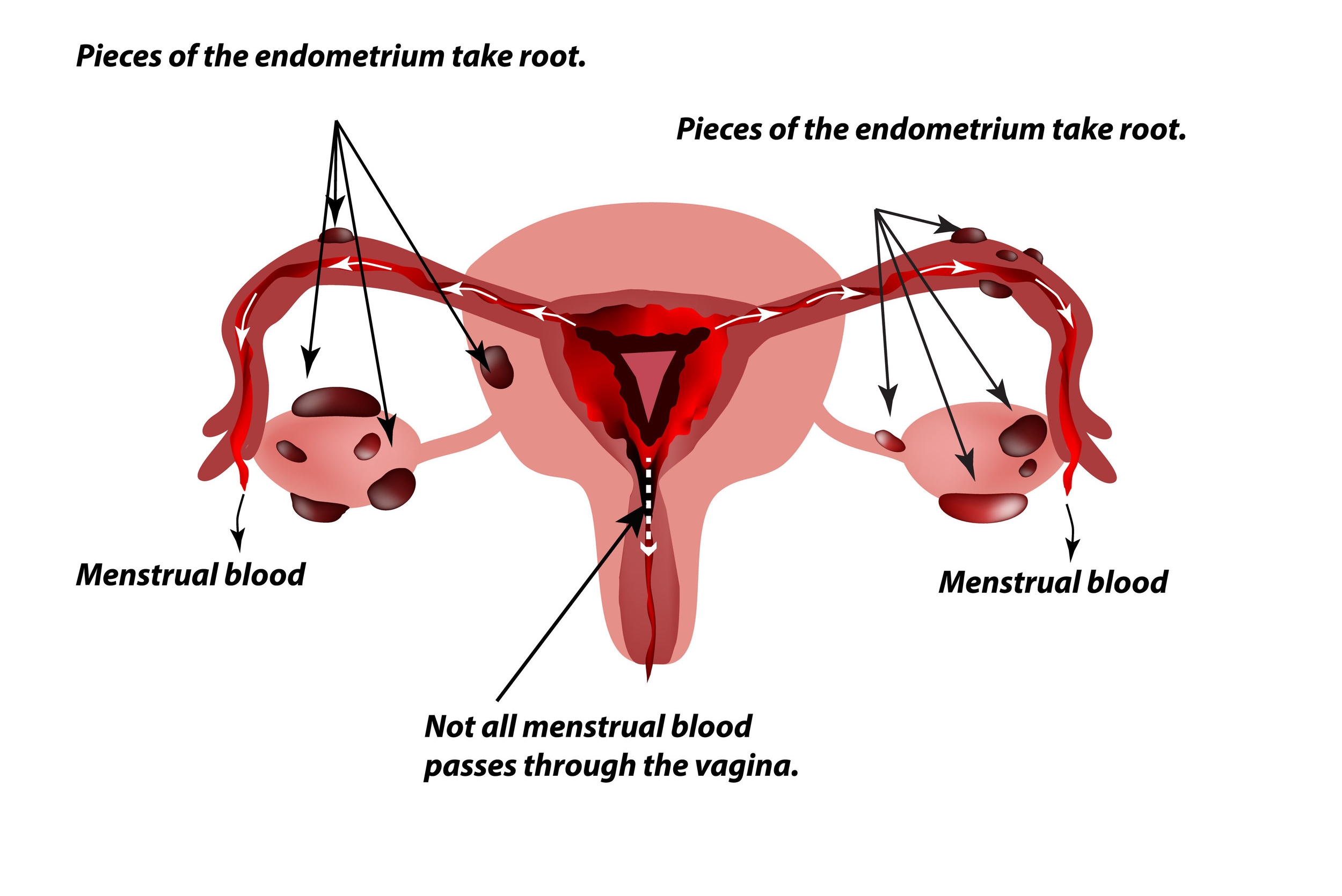
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This can include growth in the Fallopian tubes. This condition can cause significant pain and complications.
www.womensultrasoundspecialists.melbourne
Tissue Growth In Tubes
Endometriosis causes tissue to grow in the Fallopian tubes. This tissue behaves like normal uterine lining. It thickens, breaks down, and bleeds with each menstrual cycle.
This abnormal tissue growth can block the tubes. This blockage can prevent the egg from traveling. It may lead to infertility.
Pain And Complications
Endometriosis can cause severe pain. This pain often occurs during menstruation. It can also cause pain during intercourse or bowel movements.
Other complications include:
- Infertility: Blocked Fallopian tubes can prevent pregnancy.
- Ovarian Cysts: These can form as a result of endometriosis.
- Scar Tissue: Can form from repeated tissue growth and breakdown.
The pain and complications from endometriosis can be life-disrupting. Treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Tubal Ligation
Tubal ligation, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” is a surgical procedure. It permanently prevents pregnancy by blocking or sealing the fallopian tubes. This method is a popular form of female sterilization.
Procedure Overview
The tubal ligation procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia. It typically takes 30 minutes. Here’s a step-by-step overview:
- A small incision is made near the belly button.
- A laparoscope is inserted to view the fallopian tubes.
- The tubes are then cut, tied, or sealed using clips or rings.
- The incision is closed with stitches or surgical tape.
Patients can often go home the same day. Recovery time is usually short, and normal activities can be resumed in a week.
Reversibility And Effects
Tubal ligation is considered a permanent form of birth control. Reversal is possible but not guaranteed to be successful. The success rate of reversal depends on several factors, including:
- Age of the woman
- Type of tubal ligation performed
- Time elapsed since the procedure
Reversal involves reconnecting the blocked segments of the tubes. It is a more complex and expensive surgery. The effects of tubal ligation include:
| Positive Effects | Negative Effects |
|---|---|
| Permanent contraception | Not easily reversible |
| No need for hormonal birth control | Possible surgical risks |
| Minimal recovery time | Potential for regret |
Important Note: Discuss all options with a healthcare provider. Ensure this is the right choice for you.
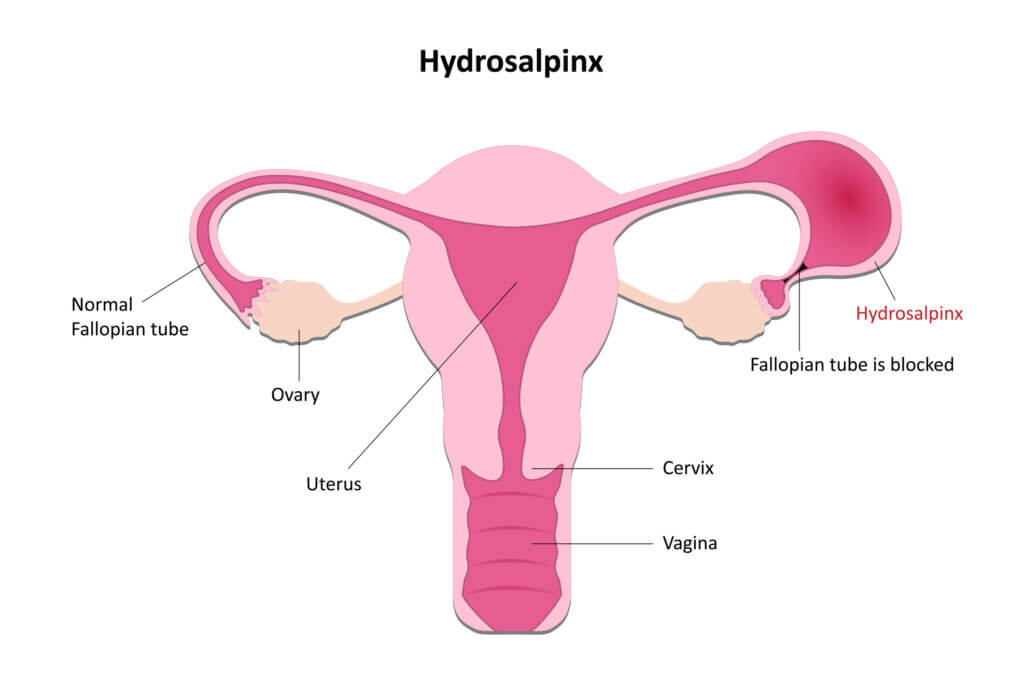
Hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx refers to a condition where the fallopian tube is filled with fluid. This fluid buildup can cause the tube to become swollen. It often results in infertility and pelvic pain. Women with hydrosalpinx may face challenges in conceiving. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial.
www.fertilityanswers.com
Fluid Accumulation
Fluid accumulation in the fallopian tube happens due to blockage. The blocked tube fills with a watery fluid. This fluid can be clear or cloudy. The blockage often results from infections or pelvic inflammatory disease. The swollen tube can be painful and may cause discomfort.
Key causes of fluid accumulation include:
- Previous pelvic infections
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Endometriosis
- Past surgeries in the pelvic area
Treatment Options
Treating hydrosalpinx involves addressing the underlying cause. Several treatment options are available.
Non-surgical treatments:
- Antibiotics: Used to treat infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications: Help reduce swelling and pain
Surgical treatments:
- Salpingectomy: Removal of the affected tube
- Salpingostomy: Creating an opening in the tube to drain fluid
- Tubal ligation: Blocking the tube to prevent fluid buildup
Fertility treatments:
- In vitro fertilization (IVF): Bypasses the fallopian tubes
| Treatment | Purpose | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | Treat infection | Oral or intravenous |
| Anti-inflammatory medications | Reduce swelling | Oral |
| Salpingectomy | Remove affected tube | Surgical |
| IVF | Assist in conception | Medical procedure |
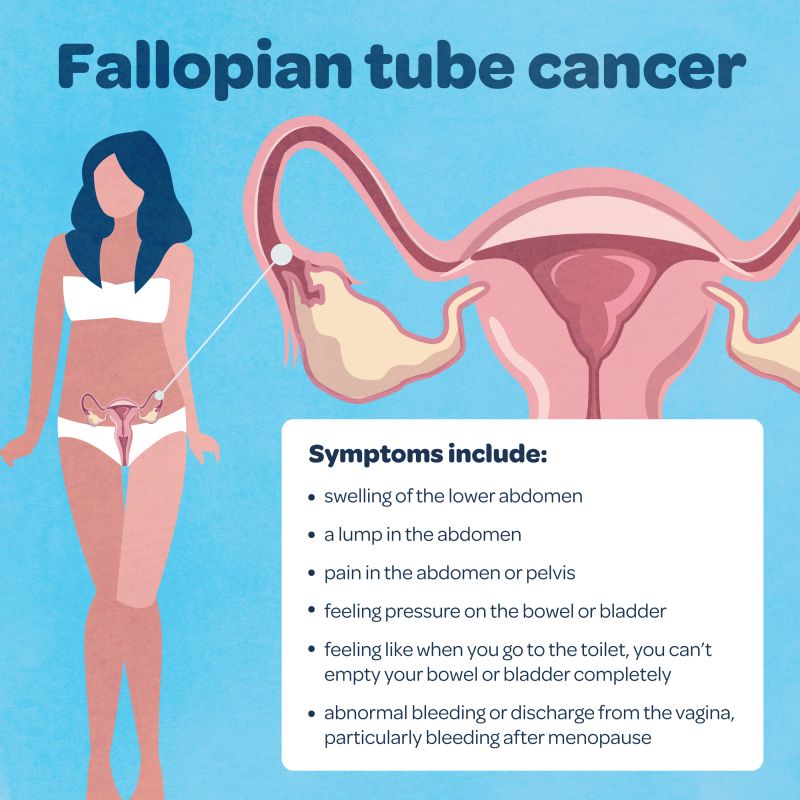
Cancer Of The Fallopian Tubes
Cancer of the Fallopian Tubes is a rare condition affecting the female reproductive system. This type of cancer begins in the fallopian tubes, which connect the ovaries to the uterus. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
www.facebook.com/QLDHealth
Types And Stages
There are different types of fallopian tube cancer, each with unique characteristics.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary | Starts in the fallopian tubes. |
| Secondary | Spreads from other parts of the body. |
Fallopian tube cancer is also categorized into various stages:
- Stage I: Cancer is limited to one or both fallopian tubes.
- Stage II: Cancer has spread to nearby pelvic organs.
- Stage III: Cancer extends to the abdomen.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs.
Symptoms And Screening
Symptoms of fallopian tube cancer can be subtle and easily overlooked. Common symptoms include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Unusual vaginal discharge
- Abdominal bloating
Screening for fallopian tube cancer involves several methods:
- Pelvic Exam: A doctor checks for abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Imaging tests to look at the fallopian tubes.
- CT or MRI: Detailed images of the pelvic area.
- Blood Tests: Checking for cancer markers.
Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis for those with fallopian tube cancer. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and screening options.
Surgical Interventions
Fallopian tubes play a crucial role in female fertility. Sometimes, surgical interventions become necessary. This section covers key procedures involving the fallopian tubes.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgery. It involves small incisions and a camera. Surgeons use it to diagnose or treat issues in the fallopian tubes.
This method has several benefits:
- Less pain post-surgery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Quicker recovery
Conditions often treated with laparoscopy include:
- Endometriosis
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Tubal blockage
Laparoscopy offers a clear view of the reproductive organs. This helps in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
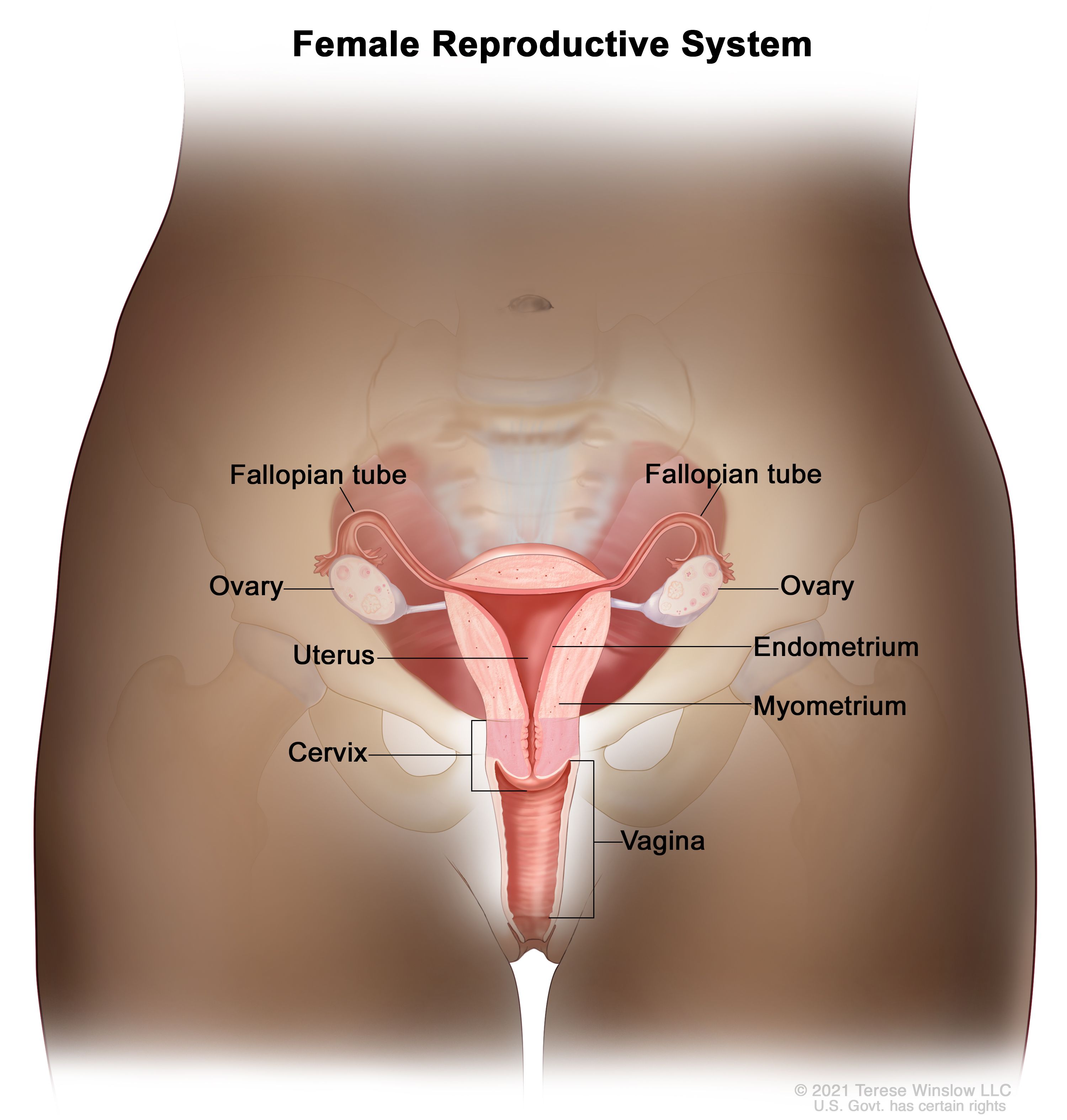
Salpingectomy
A salpingectomy involves removing one or both fallopian tubes. This procedure is necessary for various conditions.
Common reasons for salpingectomy include:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Severe infection
- Risk of ovarian cancer
There are two types of salpingectomy:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Unilateral | One fallopian tube is removed. |
| Bilateral | Both fallopian tubes are removed. |
This surgery can impact fertility. Discuss options with your doctor.
Credit: www.cancer.gov
Diagnostic Procedures
Checking the health of fallopian tubes is essential for women’s reproductive health. Various diagnostic procedures help doctors identify any problems. These tests help in planning the best treatment.
Hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is an X-ray test. It checks the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes. A special dye is used in this test. The dye helps highlight the fallopian tubes on X-ray images.
The procedure involves:
- Inserting a thin tube into the cervix.
- Injecting the dye through the tube.
- Taking X-ray images as the dye moves through the uterus and tubes.
HSG can show blockages or other problems. It is usually done in a hospital or clinic. The test takes about 30 minutes.
Laparoscopic Examination
Laparoscopic examination is a surgical procedure. It allows doctors to look directly at the fallopian tubes. A small incision is made in the abdomen. A thin tube with a camera, called a laparoscope, is inserted.
The procedure includes:
- Making a small cut near the belly button.
- Inserting the laparoscope to view the fallopian tubes.
- Using special instruments to fix any problems if needed.
Laparoscopy is done under general anesthesia. It may require a short hospital stay. This test can also help diagnose endometriosis, fibroids, or scar tissue.
Alternative Treatments
The Fallopian tubes are essential for female fertility. Blocked or damaged tubes can lead to infertility. While surgery is a common solution, alternative treatments are also available. These treatments can be less invasive and more natural. Here, we explore some of these alternative treatments.
Medications
Medications can help treat Fallopian tube issues. Doctors may prescribe antibiotics to clear infections. Anti-inflammatory drugs can reduce inflammation and swelling. Hormonal medications can help balance hormones and improve tube function. Always consult a doctor before starting any medication.
Natural Remedies
Many prefer natural remedies for treating Fallopian tube problems. Herbal treatments are popular for their healing properties. Some effective herbs include:
- Ginger: Reduces inflammation and boosts circulation.
- Garlic: Known for its antibacterial properties.
- Turmeric: Contains curcumin which reduces inflammation.
Another natural remedy is castor oil packs. These packs can improve blood flow and reduce inflammation. To use, soak a cloth in castor oil, place it on the abdomen, and cover with a warm towel. Apply for 30-60 minutes, several times a week.
Acupuncture is another alternative treatment. It can improve blood flow to the reproductive organs. Many women find relief from symptoms with regular sessions.
Diet changes can also help. Include more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and limit sugar intake. A balanced diet supports overall reproductive health.
Maintaining Tubal Health
The Fallopian tubes play a vital role in female reproductive health. They are pathways for eggs to travel from the ovaries to the uterus. Ensuring their health is essential for fertility and overall well-being. This section covers key aspects of maintaining tubal health.
Preventive Measures
Prevention is better than cure. Simple steps can maintain the health of your Fallopian tubes.
- Practice safe sex to avoid infections.
- Avoid smoking as it harms reproductive organs.
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in vitamins and minerals.
- Exercise regularly to boost overall health.
Regular Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are crucial. They help detect issues early.
| Check-Up Type | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Pelvic Exam | Annually |
| Ultrasound | As advised by your doctor |
| Blood Tests | Annually |
Early detection of problems can lead to effective treatment. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Credit: positivestepsfertility.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Function Of The Fallopian Tubes?
The fallopian tubes transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. They are also the site of fertilization.
Can You Still Get Pregnant Without Fallopian Tubes?
Yes, pregnancy is still possible without fallopian tubes through IVF, where eggs are fertilized outside the body and implanted into the uterus.
Why Would A Woman Need Her Fallopian Tubes Removed?
A woman may need her fallopian tubes removed due to ectopic pregnancy, cancer risk, infection, or severe damage. This procedure helps prevent certain health issues and can be part of sterilization. Always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
How Many Fallopian Tubes Do You Have?
Humans typically have two fallopian tubes. These tubes connect the ovaries to the uterus, allowing for the passage of eggs.
Conclusion
Understanding fallopian tubes is crucial for women’s reproductive health. Healthy tubes can aid in conception. Regular check-ups and awareness can prevent complications. Stay informed and proactive about your health. This knowledge empowers you to make better decisions for your well-being.
 Reproductive Health Sexual and Reproductive Health
Reproductive Health Sexual and Reproductive Health






