
Reproductive aging refers to the gradual decline in reproductive function with age. It affects both men and women, but more significantly impacts women.
As women age, their ovarian reserve diminishes, leading to a decrease in fertility. Men experience changes too, including reduced sperm quality and testosterone levels. This aging process can lead to challenges in conceiving and an increased risk of complications during pregnancy.
Understanding reproductive aging is crucial for making informed decisions about family planning. Early awareness and proactive health measures can help manage its effects. Consulting healthcare professionals can provide guidance tailored to individual needs. By recognizing the signs and implications of reproductive aging, individuals can better navigate their reproductive health journey.
What Is Reproductive Aging?
Reproductive aging is a natural process that affects everyone. It refers to the changes in the reproductive system as people grow older. Understanding these changes is important for maintaining health and well-being. So, what is reproductive aging?
Definition And Explanation
Reproductive aging is the gradual decline in reproductive function over time. This process impacts both men and women, but it is more noticeable in women. As people age, their bodies undergo various changes that affect their ability to reproduce.
In women, reproductive aging begins in their late 20s to early 30s. By the age of 35, the decline becomes more significant. For men, the process is slower, but it still affects their reproductive health.
- Reduction in the number of eggs
- Decreased sperm quality
- Changes in hormone levels
Understanding reproductive aging helps people make informed decisions about family planning and fertility treatments. It also helps in recognizing the signs of aging and seeking medical advice when needed.

www.nursingtimes.net
Biological Changes
Reproductive aging involves several biological changes. These changes impact the reproductive organs and their functions.
In women:
- Ovaries produce fewer eggs
- Egg quality decreases
- Menstrual cycles become irregular
In men:
- Sperm count decreases
- Sperm motility reduces
- DNA fragmentation in sperm increases
Biological changes affect fertility and the ability to conceive. They also increase the risk of genetic abnormalities in offspring. Understanding these changes helps people manage their reproductive health better.
Hormonal Shifts
Hormonal shifts play a crucial role in reproductive aging. These shifts impact various bodily functions and overall health.
In women:
- Decrease in estrogen and progesterone
- Increase in follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Onset of menopause
In men:
- Reduction in testosterone levels
- Increase in luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Changes in libido and sexual function
Hormonal shifts affect mood, energy levels, and overall well-being. They also influence the likelihood of developing age-related diseases. Monitoring hormone levels and seeking medical advice can help manage these shifts effectively.
Signs Of Aging
Reproductive aging is a natural process that affects everyone. As women age, their reproductive system undergoes significant changes. Recognizing the signs of aging can help manage expectations and plan accordingly. These signs often appear in different aspects of a woman’s reproductive health.
Menstrual Cycle Changes
One of the earliest signs of reproductive aging is changes in the menstrual cycle. Women might notice irregular periods. These changes can include:
- Shorter cycles (less than 21 days)
- Longer cycles (more than 35 days)
- Heavier or lighter bleeding
- Skipped periods
These variations occur because the ovaries start producing fewer hormones. Estrogen and progesterone levels fluctuate during this time. This fluctuation causes the menstrual cycle to become unpredictable.
A table summarizing menstrual cycle changes:
| Change | Description |
|---|---|
| Shorter Cycles | Less than 21 days |
| Longer Cycles | More than 35 days |
| Heavier Bleeding | More blood loss than usual |
| Lighter Bleeding | Less blood loss than usual |
| Skipped Periods | Periods that do not occur |
Tracking these changes can help. Consult a healthcare professional if you notice significant alterations. They can provide guidance and support during this time.
Fertility Decline
Another major sign of reproductive aging is a decline in fertility. Fertility begins to decline in a woman’s early 30s and accelerates in her late 30s and 40s. This decline happens because:
- The number of available eggs decreases
- Egg quality diminishes over time
- Hormonal changes affect ovulation
Here is a table showcasing fertility decline with age:
| Age | Fertility Rate |
|---|---|
| 20-24 | Peak fertility |
| 25-29 | Slight decline |
| 30-34 | Noticeable decline |
| 35-39 | Significant decline |
| 40+ | Sharp decline |
Fertility decline is a natural process. Understanding this decline can help in family planning. Women can seek fertility treatments if needed. Options include IVF, egg freezing, and more. Consulting a fertility specialist is recommended.
Impact On Women
Reproductive aging significantly impacts women. As women age, their reproductive systems undergo changes that can affect their overall health and quality of life. Understanding these changes can help women prepare for and manage the effects of reproductive aging.
Menopause Timeline
Menopause typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55. The timeline of menopause varies for each woman but usually follows a predictable pattern. The stages include:
- Perimenopause: This stage can start 8 to 10 years before menopause. Women may experience irregular periods, hot flashes, and mood swings.
- Menopause: Officially begins 12 months after a woman’s last menstrual period. Symptoms include night sweats, vaginal dryness, and sleep problems.
- Postmenopause: This stage begins after menopause. Symptoms may continue for several years, but the risk for certain health conditions increases.
Here is a table summarizing the menopause stages:
| Stage | Age Range | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Perimenopause | 35-45 | Irregular periods, hot flashes, mood swings |
| Menopause | 45-55 | Night sweats, vaginal dryness, sleep problems |
| Postmenopause | 55+ | Ongoing symptoms, increased health risks |
Health Risks
Reproductive aging increases the risk of several health conditions. Women should be aware of these risks to take proactive steps for their health.
- Osteoporosis: Decreased estrogen levels can lead to bone density loss, increasing fracture risk.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Postmenopausal women have a higher risk of heart disease due to changes in blood vessels and cholesterol levels.
- Weight Gain: Hormonal changes can slow metabolism, leading to weight gain and obesity.
- Diabetes: Insulin resistance may increase, raising the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Women should adopt a healthy lifestyle to mitigate these risks. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and routine check-ups are crucial. Here is a quick guide:
- Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of physical activity daily.
- Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Check-ups: Schedule regular medical check-ups for early detection and management of health issues.
Understanding reproductive aging helps women navigate this natural process with confidence and health.
Credit: www.aging-us.com
Impact On Men
Reproductive aging affects both men and women, but it impacts men differently. As men age, changes in reproductive health can influence their overall well-being. Understanding these changes is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Sperm Quality
As men grow older, sperm quality tends to decline. This change can affect fertility and the health of potential offspring. Key factors influencing sperm quality include:
- Motility: The ability of sperm to move efficiently decreases with age.
- Morphology: The shape and structure of sperm may become abnormal.
- DNA Integrity: Older sperm may have more DNA fragmentation.
Research indicates that men over 40 face a higher risk of fathering children with genetic abnormalities. A study found that DNA fragmentation rates in sperm increase significantly after age 45. This can lead to higher miscarriage rates and developmental issues in children.
Here is a table summarizing the changes in sperm quality with age:
| Age Group | Motility (%) | Normal Morphology (%) | DNA Fragmentation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20-30 | 60-70 | 15-20 | 10-15 |
| 31-40 | 50-60 | 10-15 | 15-20 |
| 41-50 | 40-50 | 5-10 | 20-25 |
| 51+ | 30-40 | 5 | 25-30 |
Testosterone Levels
Testosterone levels gradually decrease as men age. This hormone is crucial for maintaining muscle mass, bone density, and sexual function. A decline in testosterone can lead to various health issues.
Common symptoms of low testosterone include:
- Reduced libido
- Fatigue
- Depression
- Decreased muscle mass
- Increased body fat
Studies show that men over 30 experience a 1% drop in testosterone levels each year. By age 70, a man’s testosterone level may be only 60% of his peak level in his 20s.
Below is a table showing average testosterone levels by age:
| Age Group | Average Testosterone Level (ng/dL) |
|---|---|
| 20-30 | 600-700 |
| 31-40 | 500-600 |
| 41-50 | 400-500 |
| 51-60 | 300-400 |
| 61-70 | 200-300 |
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the effects of declining testosterone. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep are essential.
Emotional Effects
Reproductive aging is a natural process. It affects everyone differently. The emotional effects of reproductive aging can be profound. Understanding these effects helps in managing them better. Let’s explore how reproductive aging impacts mental health and relationship dynamics.
Mental Health
Reproductive aging can have a significant impact on mental health. Many people experience anxiety and depression during this time. Hormonal changes play a big role in these feelings. The decline in estrogen levels can affect mood.
Some common emotional symptoms include:
- Mood swings
- Sadness
- Increased irritability
- Sleep disturbances
It’s important to recognize these symptoms. Seeking help from mental health professionals can be beneficial. There are also many self-care practices that can help:
- Regular exercise
- Healthy diet
- Mindfulness and meditation
- Connecting with loved ones
The table below highlights some effective strategies for managing mental health during reproductive aging:
| Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Reduces stress and improves mood |
| Healthy diet | Balances hormones and boosts energy |
| Mindfulness | Improves emotional regulation |
| Social support | Provides emotional comfort |
Relationship Dynamics
Reproductive aging can also affect relationship dynamics. Partners may find it challenging to navigate this phase together. Open communication is crucial during this time. Couples should talk about their feelings and concerns.
Some common relationship challenges include:
- Changes in intimacy
- Emotional distance
- Different coping mechanisms
Here are some tips for maintaining a healthy relationship:
- Have regular, honest conversations
- Spend quality time together
- Seek couple’s therapy if needed
- Be patient and understanding
The table below provides some practical tips for couples:
| Tip | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Regular conversations | Helps in understanding each other’s feelings |
| Quality time | Strengthens the bond |
| Couple’s therapy | Offers professional guidance |
| Patience | Creates a supportive environment |
By understanding these emotional effects, individuals and couples can better navigate the challenges of reproductive aging.
Lifestyle Factors
Reproductive aging is a natural process that affects everyone. Lifestyle factors play a significant role in how our bodies age, including our reproductive systems. Understanding how nutrition and exercise can impact reproductive aging can help individuals make better choices to support their reproductive health.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays a crucial role in reproductive aging. A well-balanced diet can help maintain hormone levels and support overall reproductive health. Here are some key dietary elements to consider:
- Antioxidants: Foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens, help combat oxidative stress. This stress can accelerate aging, including reproductive aging.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flax seeds, and walnuts, support hormone production. These fats are essential for maintaining reproductive health.
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice provide essential nutrients and fiber. They help regulate blood sugar levels, which is important for hormonal balance.
- Lean Proteins: Lean proteins, such as chicken, turkey, and legumes, support muscle health and hormone production. Adequate protein intake is vital for reproductive health.
| Food Category | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Antioxidants | Berries, Nuts, Leafy Greens | Combats oxidative stress |
| Healthy Fats | Fish, Flax Seeds, Walnuts | Supports hormone production |
| Whole Grains | Oats, Quinoa, Brown Rice | Regulates blood sugar levels |
| Lean Proteins | Chicken, Turkey, Legumes | Supports muscle health |
By focusing on these nutritional elements, individuals can support their reproductive health and potentially slow down reproductive aging.
Exercise
Exercise is another important lifestyle factor that impacts reproductive aging. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial for hormonal balance. Here are some benefits of exercise:
- Improves Circulation: Exercise increases blood flow to reproductive organs. This can enhance their function and delay aging.
- Reduces Stress: Physical activity helps reduce stress levels. Lower stress means better hormonal balance, which supports reproductive health.
- Maintains Healthy Weight: Regular exercise helps manage weight. Being overweight or underweight can negatively affect reproductive health.
- Boosts Mood: Exercise releases endorphins that improve mood. A positive mood can support overall well-being, including reproductive health.
Here is a simple weekly exercise plan:
| Day | Activity | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Walking | 30 minutes |
| Tuesday | Yoga | 45 minutes |
| Wednesday | Jogging | 30 minutes |
| Thursday | Strength Training | 40 minutes |
| Friday | Swimming | 30 minutes |
| Saturday | Cycling | 45 minutes |
| Sunday | Rest | – |
Following this exercise plan can help maintain a healthy weight and support reproductive health. Regular activity can slow down reproductive aging and promote overall well-being.
Understanding the Male Reproductive System: Key Anatomy & Health Tips
Medical Advances
Reproductive aging is a natural process that affects both men and women as they grow older. With age, fertility declines, making it harder to conceive. Thankfully, medical advances have made it possible to combat some of these challenges. Breakthroughs in fertility treatments and hormone therapy are giving hope to many who wish to start or grow their families.
Fertility Treatments
Fertility treatments have seen significant progress in recent years. These treatments aim to help individuals and couples overcome reproductive challenges. Here are some of the most notable advancements:
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF involves retrieving eggs and sperm, combining them in a lab, and transferring the embryo to the uterus. This method has helped millions conceive.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): This technique involves injecting a single sperm directly into an egg. It is particularly useful for male infertility issues.
- Egg Freezing: Women can now freeze their eggs to preserve fertility for future use. This is especially beneficial for those delaying childbirth.
Recent advancements have also improved the success rates of these treatments:
| Fertility Treatment | Success Rate |
|---|---|
| IVF | Up to 40% |
| ICSI | 40-50% |
| Egg Freezing | 70-90% (thaw survival) |
These treatments are becoming more accessible, offering new hope to many.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy is another area where significant advancements have been made. This therapy helps balance hormone levels, improving reproductive health. Here are some key aspects:
- Estrogen Therapy: This treatment can help alleviate symptoms of menopause, such as hot flashes and vaginal dryness.
- Progesterone Therapy: Progesterone is often used alongside estrogen to reduce the risk of uterine cancer in women undergoing hormone therapy.
- Testosterone Therapy: For men, testosterone therapy can address symptoms of low testosterone, such as decreased libido and energy levels.
Hormone therapy offers a variety of benefits:
| Hormone Therapy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Estrogen Therapy | Reduces menopausal symptoms, improves bone health |
| Progesterone Therapy | Balances estrogen, protects uterine health |
| Testosterone Therapy | Increases libido, boosts energy levels |
These treatments are tailored to individual needs, making them highly effective.
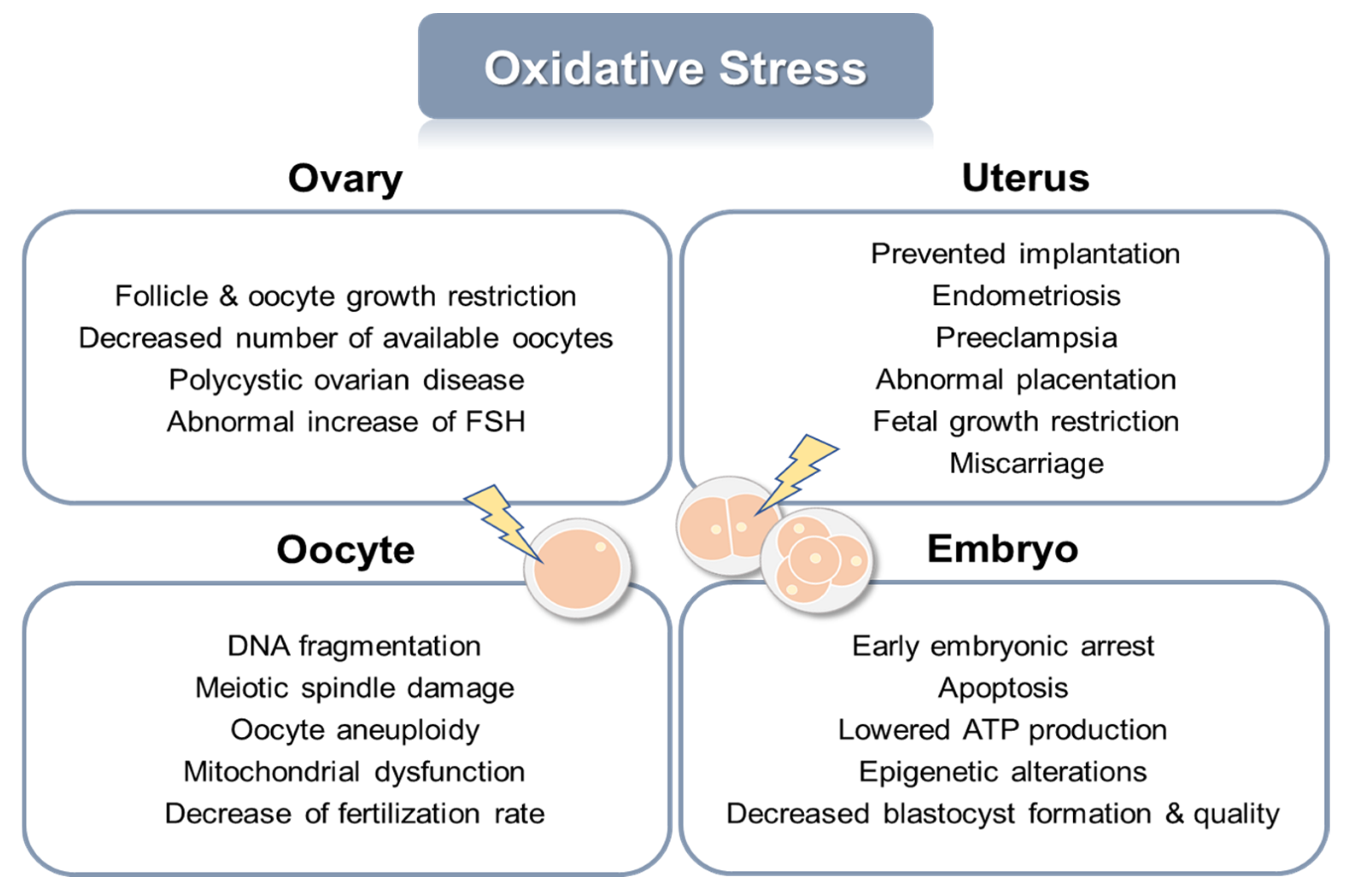
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Future Research
Reproductive aging is a natural process that affects everyone. Researchers are exploring new ways to understand this phenomenon better. Future research aims to bring groundbreaking advancements in reproductive health. Scientists are working hard to uncover the mysteries of aging and genetics. These insights will help improve health outcomes for many people.
Innovations In Reproductive Health
Innovations in reproductive health are transforming lives. New technologies and research methods are leading the way. Here are some of the exciting developments:
- Fertility Preservation: Techniques like egg freezing are becoming more reliable. This helps people plan their families better.
- Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell research is showing promise. It may help rejuvenate aging reproductive organs.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Early detection of reproductive issues is now possible. This leads to timely treatment and better outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Treatments are becoming more tailored. This increases the chances of success for each individual.
Researchers are also focusing on non-invasive methods to monitor reproductive health. Wearable devices and mobile apps are becoming popular. These tools help track important health metrics.
| Innovation | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fertility Preservation | Allows family planning |
| Regenerative Medicine | Rejuvenates organs |
| Advanced Diagnostics | Early issue detection |
| Personalized Medicine | Tailored treatments |
These innovations are paving the way for a healthier future. They offer hope and new possibilities for many individuals.
Aging And Genetics
Aging and genetics play a crucial role in reproductive health. Genetic research is uncovering how our genes affect aging. Scientists are identifying key genetic markers that influence reproductive aging.
Understanding these markers can lead to targeted therapies. Here are some of the areas of focus:
- Genetic Mapping: Scientists are mapping genes linked to aging. This helps in identifying at-risk individuals.
- Gene Editing: Techniques like CRISPR are being explored. They may help correct genetic issues affecting reproduction.
- Epigenetics: Researchers are studying how lifestyle affects gene expression. This can lead to personalized health advice.
- Biomarkers: Identifying biomarkers helps in early diagnosis. This can improve treatment outcomes.
Genetic research is also exploring the role of mitochondria in aging. These cellular powerhouses are crucial for reproductive health. Maintaining mitochondrial health can slow down the aging process.
By understanding the genetic basis of aging, researchers can develop preventive strategies. This knowledge can help people lead healthier lives as they age.
References/further Reading
Understanding reproductive aging is crucial for managing health and wellness. This section offers valuable references for further reading. These resources provide deep insights into the science and implications of reproductive aging.
Books On Reproductive Aging
- “The Menopause Manifesto” by Dr. Jen Gunter – A comprehensive guide on menopause and aging.
- “The Wisdom of Menopause” by Dr. Christiane Northrup – Explores the physical and emotional aspects of menopause.
- “Estrogen Matters” by Avrum Bluming and Carol Tavris – Discusses the role of estrogen in aging and health.
Scientific Journals And Articles
| Title | Author(s) | Journal |
|---|---|---|
| Reproductive Aging and Its Implications | Smith et al. | Journal of Women’s Health |
| Hormonal Changes and Menopause | Johnson et al. | Endocrinology Review |
| Ovarian Aging and Fertility | Brown et al. | Fertility Science |
Websites And Online Resources
- Mayo Clinic – Offers detailed articles on menopause and aging.
- WebMD – Provides information on symptoms and treatments.
- Women’s Health – Government resource on women’s health issues.
Podcasts And Videos
- “The Menopause Podcast” – Hosted by experts discussing menopause.
- “Aging and Reproduction” – TED Talk by Dr. Jane Smith.
- “Reproductive Health” – YouTube series by Dr. Emily Brown.
Credit: www.aging-us.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Reproductive Aging?
Reproductive aging refers to the natural decline in reproductive function as one ages. It affects fertility and hormone levels.
What Are The Indicators Of Reproductive Aging?
Indicators of reproductive aging include irregular menstrual cycles, decreased fertility, hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. Hormonal changes, such as lower estrogen levels, also signal aging. Reduced egg quality and quantity are common signs. These symptoms often begin in a woman’s late 30s to early 40s.
What Are The Stages Of Reproductive Ageing?
The stages of reproductive aging include premenopause, perimenopause, menopause, and postmenopause. Premenopause involves regular cycles, perimenopause features irregular cycles, menopause marks the end of menstrual cycles, and postmenopause follows menopause.
What Is Considered Reproductive Age?
Reproductive age typically ranges from puberty to menopause. For most women, it’s between ages 15 and 49.
Conclusion
Reproductive aging is a natural process affecting everyone. Understanding it helps in making informed health decisions. Staying proactive about reproductive health is crucial. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can make a difference. Embrace the changes and seek professional advice when needed.
Your journey through reproductive aging can be manageable and empowering.
 Reproductive Health Sexual and Reproductive Health
Reproductive Health Sexual and Reproductive Health






